Introduction
When it comes to selecting materials for construction, engineering, or DIY projects, choosing the right type can make all the difference. Two popular materials are fiberglass angle strips and aluminum. Each offers distinct advantages and is suited for different applications. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the pros and cons of both materials, comparing them on various factors to help you make an informed decision.
fiberglass angle strips
Understanding Fiberglass Angle Strips
What Are Fiberglass Angle Strips?
Fiberglass angle strips are structural elements made from a composite material consisting of glass fibers embedded in a resin matrix. They are known for their high strength-to-weight ratio and resistance to corrosion.
Properties of Fiberglass
- Lightweight: Fiberglass is much lighter than metals like aluminum.
- High Strength: Despite being lightweight, it has excellent tensile strength.
- Corrosion Resistance: Fiberglass doesn’t rust or corrode, making it ideal for harsh environments.
- Electrical Insulation: It is non-conductive, which is beneficial in electrical applications.
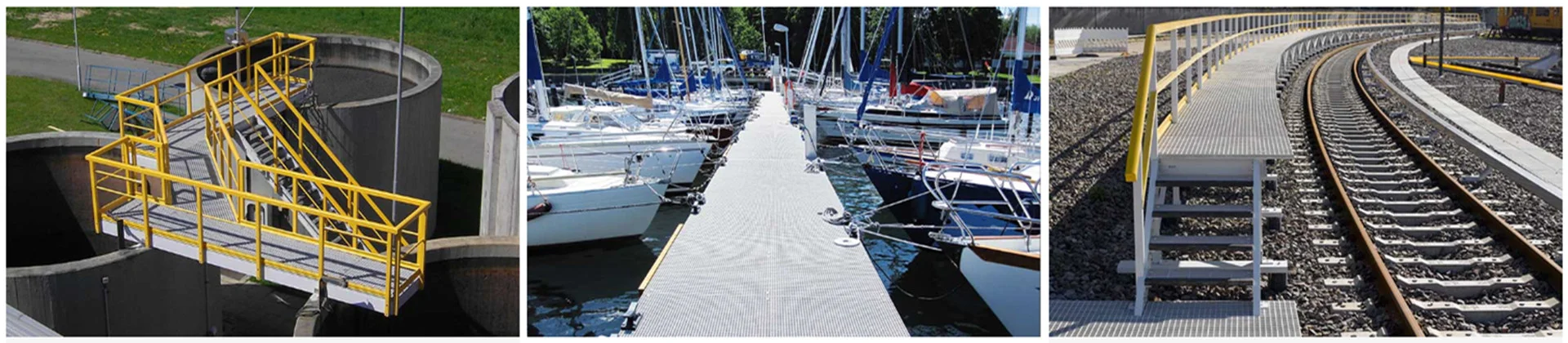
Applications of Fiberglass Angle Strips
- Construction: Used in building frameworks and reinforcements.
- Marine Industry: Ideal for boat construction due to its resistance to saltwater.
- Electrical: Utilized in electrical enclosures and supports.
- Automotive: Used in the manufacturing of car parts to reduce weight.
Understanding Aluminum Angle Strips
What Are Aluminum Angle Strips?
Aluminum angle strips are structural elements made from aluminum, known for their versatility and strength. Aluminum is a lightweight metal with a natural resistance to corrosion.
Properties of Aluminum
- Lightweight: Aluminum is lightweight, though typically heavier than fiberglass.
- High Strength: Aluminum has good strength but is generally less strong than fiberglass for the same weight.
- Corrosion Resistance: It naturally forms a protective oxide layer that prevents corrosion.
- Thermal Conductivity: Aluminum has high thermal conductivity, making it useful in heat transfer applications.
Applications of Aluminum Angle Strips
- Construction: Commonly used in building frames and structural supports.
- Aerospace: Essential in aircraft construction due to its strength and weight.
- Automotive: Used in manufacturing car frames and body parts.
- Household: Found in furniture, appliances, and DIY projects.
Comparing Strength and Durability
Tensile Strength
- Fiberglass: Offers superior tensile strength, especially in weight-sensitive applications.
- Aluminum: Strong but generally lower tensile strength compared to fiberglass.
Impact Resistance
- Fiberglass: More flexible, can absorb impacts without breaking.
- Aluminum: Rigid, may dent or crack under high impact.
Corrosion Resistance
- Fiberglass: Exceptionally resistant to corrosion, ideal for marine and chemical environments.
- Aluminum: Good resistance due to oxide layer, but can corrode in certain conditions.
Cost Comparison
Material Cost
- Fiberglass: Generally more expensive due to the manufacturing process.
- Aluminum: Typically cheaper and more readily available.
Maintenance Costs
- Fiberglass: Low maintenance due to its durability and corrosion resistance.
- Aluminum: Also low maintenance but may require occasional treatment to prevent corrosion.
Weight Considerations
Weight-to-Strength Ratio
- Fiberglass: Higher strength-to-weight ratio, making it ideal for lightweight structures.
- Aluminum: Heavier than fiberglass but still offers a good weight-to-strength ratio.
Ease of Fabrication and Installation
Cutting and Shaping
- Fiberglass: Requires specialized tools and safety precautions due to dust.
- Aluminum: Easier to cut and shape using standard tools.
Joining Methods
- Fiberglass: Typically joined using adhesives or mechanical fasteners.
- Aluminum: Can be welded, bolted, or riveted easily.
Environmental Impact
Sustainability
- Fiberglass: Less environmentally friendly due to the manufacturing process and challenges in recycling.
- Aluminum: More sustainable as it is highly recyclable and requires less energy to produce when recycled.
Thermal and Electrical Properties
Thermal Conductivity
- Fiberglass: Low thermal conductivity, making it a good insulator.
- Aluminum: High thermal conductivity, useful for heat dissipation.
Electrical Conductivity
- Fiberglass: Non-conductive, ideal for electrical applications.
- Aluminum: Conductive, not suitable where electrical insulation is required.
Suitability for Specific Applications
Construction Projects
- Fiberglass: Preferred for corrosion-prone environments and where weight is a critical factor.
- Aluminum: Ideal for general construction due to its balance of strength, weight, and cost.
Marine and Chemical Environments
- Fiberglass: Superior due to its excellent corrosion resistance.
- Aluminum: Good but may require additional treatments.
Electrical and Thermal Applications
- Fiberglass: Best for electrical insulation needs.
- Aluminum: Suitable for thermal management applications.
Safety Considerations
Handling and Installation
- Fiberglass: Can cause skin irritation and respiratory issues; protective gear is necessary.
- Aluminum: Safer to handle but can have sharp edges.
Long-term Safety
- Fiberglass: Stable and safe once installed.
- Aluminum: Stable and non-toxic.
Longevity and Lifecycle
Service Life
- Fiberglass: Long service life, especially in harsh conditions.
- Aluminum: Also long-lasting but may need protection in corrosive environments.
Lifecycle Costs
- Fiberglass: Higher initial cost but lower maintenance.
- Aluminum: Lower initial cost but may have higher lifecycle costs due to potential corrosion issues.
FAQs
What is the main advantage of fiberglass angle strips over aluminum? Fiberglass angle strips offer superior corrosion resistance and a higher strength-to-weight ratio, making them ideal for environments where these factors are critical.
Are aluminum angle strips easier to work with than fiberglass? Yes, aluminum angle strips are generally easier to cut, shape, and join using standard tools and techniques compared to fiberglass, which requires specialized tools and safety precautions.
Which material is more cost-effective in the long run, fiberglass or aluminum? While fiberglass has a higher initial cost, its durability and low maintenance make it more cost-effective over time, especially in corrosive environments. Aluminum, being cheaper initially, may incur higher maintenance costs.
Can fiberglass angle strips be used in electrical applications? Yes, fiberglass is non-conductive and is therefore an excellent choice for electrical applications where insulation is needed.
Is aluminum recyclable? Yes, aluminum is highly recyclable, which makes it a more environmentally friendly option compared to fiberglass.
Which material offers better impact resistance? Fiberglass offers better impact resistance as it is more flexible and can absorb shocks without breaking, whereas aluminum is more rigid and prone to denting or cracking under impact.
Conclusion
Choosing between fiberglass angle strips and aluminum depends largely on the specific requirements of your project. Fiberglass excels in corrosive environments and where weight and strength are critical, while aluminum is more versatile, easier to work with, and often more cost-effective initially. By considering the strengths and weaknesses of each material in relation to your project needs, you can make an informed decision that ensures durability, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness.
 info@unicomposite.com
info@unicomposite.com


























