FRP pultrusion profile, as the name suggests, refers to the profile product produced by the pultrusion process. “Pultrusion” combines “pull” and “extrusion” to pultrude and stretch raw materials.
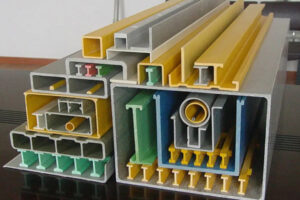
FRP pultrusion profiles
In the standard pultrusion process, glass fiber, resin, and auxiliary materials are the three major elements. First, the glass fiber is put into the resin as a reinforcing material to be soaked, and then equipped with a separate preforming system, and the resin is coagulated and polymerized through a heated fixed mold.
Impregnation can be accomplished by pulling the reinforcement through a soaking bath, or by injecting resin into an injection cavity connected to the mold. A variety of resins can be used for pultrusion, including the more common thermoset resins: polyurethane, polyester, vinyl, and epoxy, among others. Its characteristics are corrosion resistance, UV resistance, impact resistance, etc., while glass fiber provides a strength guarantee.

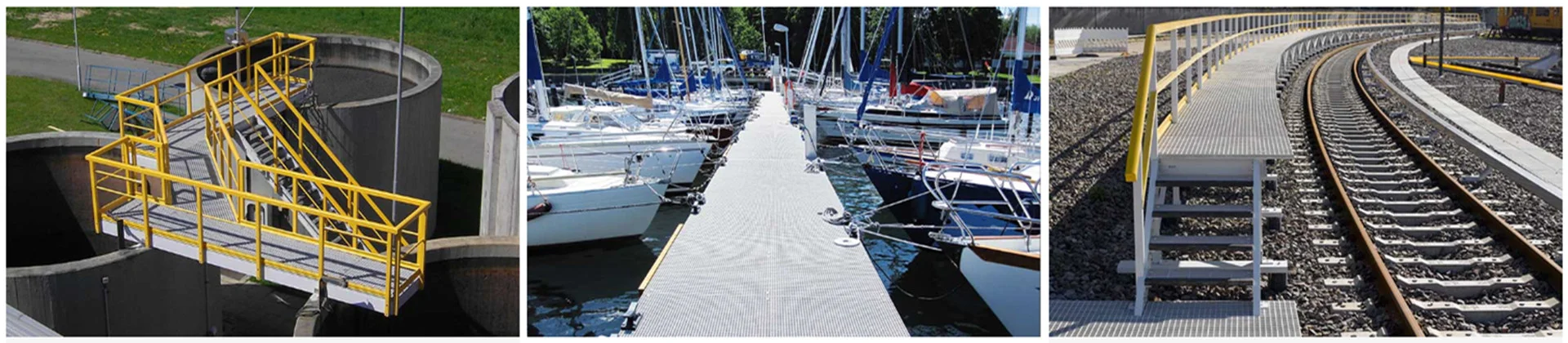
Due to these characteristics of FRP profiles, in recent years, the industrial output and the use of materials in industrialized countries have been increasing every year, coupled with the continuous innovation and development of technology, the application of various types of profiles has been promoted, especially in automobiles. In the field, the demand for this technology is particularly obvious, in addition, this product technology can also be used in the agricultural and chemical industries to manufacture FRP floors with corrosion resistance for livestock facilities and chemical plant buildings.
In the construction industry, it can be used for profiles, carcasses, reinforcing ribs for PVC windows, etc.; in the aerospace field, for the manufacture of structural components for aircraft; in sports and tourism, for the manufacture of equipment with high strength properties: skis, ski poles, golf course flagpoles, tent and shed structures, etc.; in electrical engineering, fiberglass rods for insulators and support structures for signal block components, etc.
 info@unicomposite.com
info@unicomposite.com


























