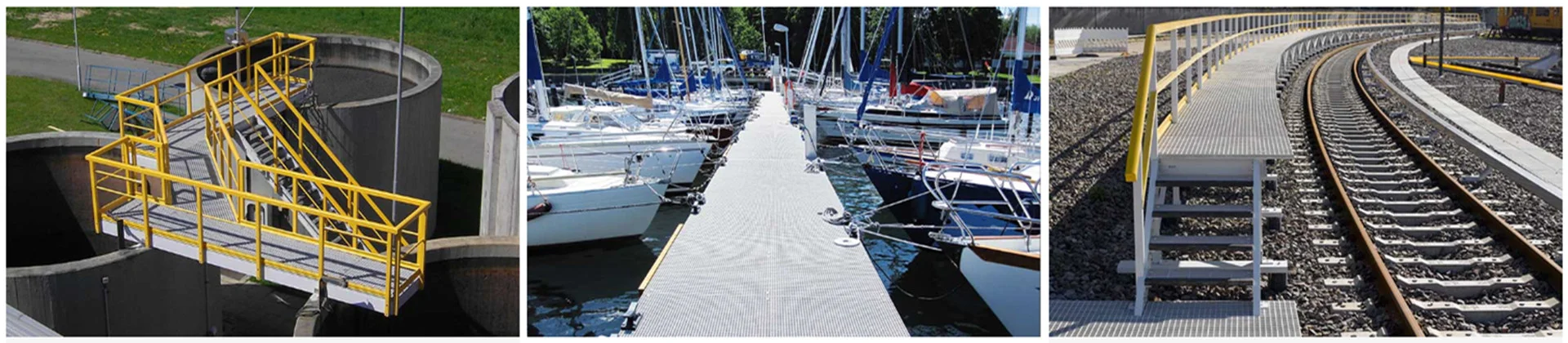
What is FRP?
Fiber-reinforced polymer (FRP) is a composite material that is widely used in many industries such as aerospace, automotive, construction, and marine. It is a versatile and durable material that is resistant to corrosion, weathering, and chemicals. FRP is made by combining two or more materials to form a composite with superior properties to the individual components. The manufacturing process of FRP involves several steps that require precise control and attention to detail.
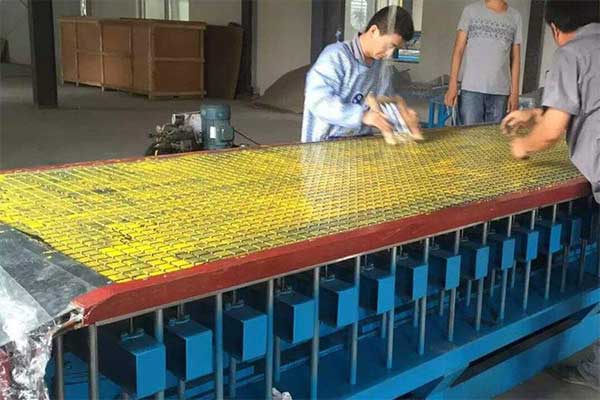

Step 1: Selection of Materials

The matrix material, which is the bulk of the composite, is usually a thermosetting resin such as polyester, epoxy, or vinyl ester. The matrix provides the composite with structural integrity, protects the fibers from damage, and transfers stresses to the fibers. The reinforcing fibers, which give the composite its strength and stiffness, can be made of glass, carbon, or aramid. The fibers are typically woven or braided into a fabric that is then impregnated with the matrix material.
Step 2: Preparation of the Mold or Tool
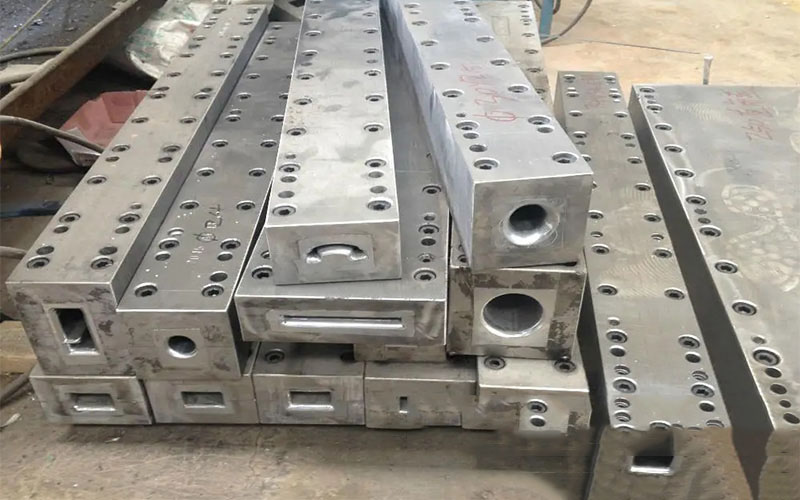
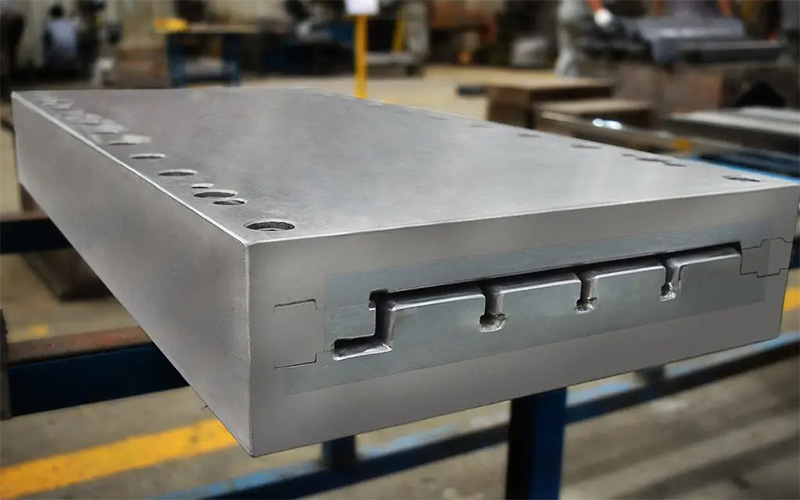



The mold determines the shape and surface finish of the composite. The mold can be made of various materials such as metal, plastic, or composite, depending on the size and complexity of the part. The mold must be cleaned, coated with a release agent, and prepared for the resin infusion process.
Step 3: The Layup or Preform Process
The layup involves cutting the fibers into the desired shape and laying them on a flat surface according to the design of the part. The fibers are arranged in a specific orientation to optimize the strength and stiffness of the composite. The preform process involves molding the fibers into a specific shape using a preform tool. The preform is then placed in the mold to begin the infusion process.
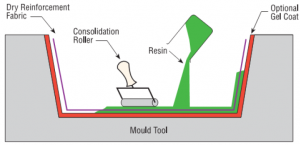
Step 4: Infusion Process
The infusion process involves saturating the fibers with the matrix material. There are several methods of infusion such as hand layup, vacuum bagging, and resin transfer molding (RTM). In hand layup, the matrix material is applied by hand to the fibers. In vacuum bagging, the fibers and matrix material are placed in a vacuum-sealed bag, and the pressure differential forces the matrix material into the fibers. In RTM, the matrix material is injected into the mold under pressure, and the fibers are impregnated with the resin.
Step 5: Curing Process
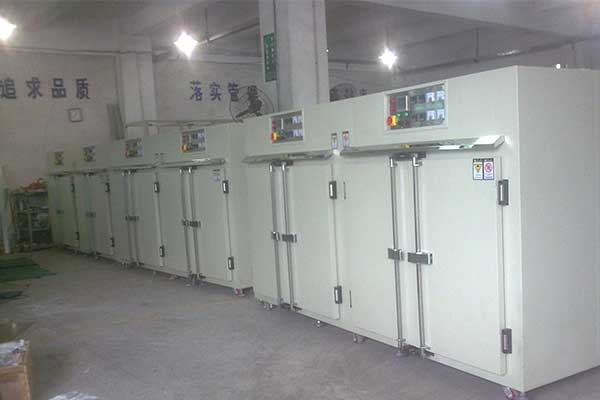

The curing process involves heating the composite to a specific temperature and holding it there for a certain time. The curing process activates the chemical reaction between the resin and the hardener, which causes the resin to crosslink and harden. The curing process can be done at room temperature or in an oven, depending on the type of resin and the size of the part.
Step 6: Finishing Process
The finishing process involves removing the part from the mold, trimming off any excess material, and sanding or polishing the surface to achieve the desired finish. The part is then inspected for defects such as voids, delamination, or surface imperfections. If any defects are found, they are repaired before the part is shipped to the customer.
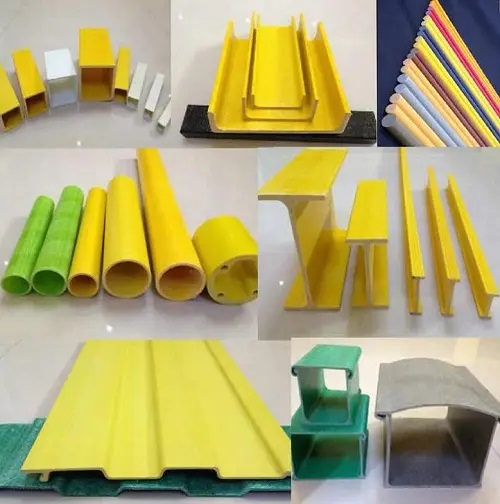



Summary
The manufacturing process of FRP is a complex and precise process that requires attention to detail and control. The selection of materials, preparation of the mold, layup or preform process, infusion process, curing process, and finishing process all play a critical role in the quality and performance of the composite. The versatility, durability, and superior properties of FRP make it a valuable material in many industries and applications.
 info@unicomposite.com
info@unicomposite.com


























